Investments, Mutual Funds
What is a Mutual Fund and What are its Benefits?
"Mutual funds were created to make investing easy, so consumers wouldn't have to be burdened with...
Exchange-traded funds or ETFs, were first designed way back in 1990, with the aim of giving retail investors access to passive indexed funds.
Since then, the ETF market has grown enormously and is now used by investors and traders worldwide.
Technological advancements and easy access to trading platforms have made ETF investment easier.
With the advent of the Covid-19 vaccine, ETFs have become more popular owing to their growth and broad diversification potential.
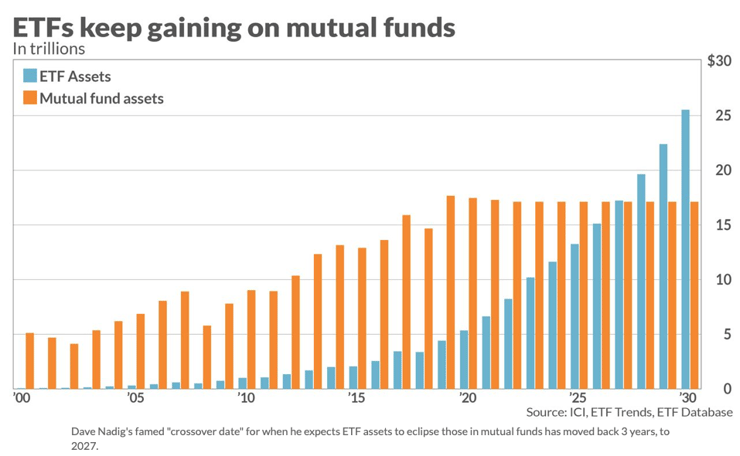
Image Source: https://www.marketwatch.com
Thanks to the sluggish global economy and dwindling job market, the need to save and invest is more pronounced than ever before.
Lower returns on fixed deposits and other asset classes are keeping investors on the back foot.
Lack of liquidity and the unforgiving nature of Real estate investment during adverse market conditions and a longer recovery cycle are significant deterrents for real estate investment.
What, then, can ETFs do for you?
An ETF is a type of investment fund that is traded on stock exchanges. Unlike mutual funds, which you may purchase and sell based on their value at the end of the day, you may transact in ETFs all through the day.
ETFs may hold different assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, and currencies. Dave Nadig, an ETF industry pioneer, opines;
“ETFs are fundamentally a technology. They are mechanisms to achieve a certain goal, like phones. Traditional mutual funds were rotary phones. ETFs are smartphones: They do the same thing but are in a better package.”
A common perception is that ETFs are low-cost, low-risk investments, and simply investing in S&P 500 ETFs guarantees good returns. While ETFs make for suitable investments, the fact remains that they are market-linked.
As a result, the risk they bear could be similar to that of other market-linked assets such as stocks, mutual funds, bonds, and commodities. What works in favor of ETFs is that they give you access to an array of asset classes at a relatively low cost.
Different types of ETFs serve specific purposes and have distinct places in investment portfolios. Your main options include:
Some of the other popular ETFs include real estate ETFs, bond ETFs, dividend ETFs, factor ETFs, and sustainable ETFs.
Depending on the ETF you invest in, you may stand to receive dividends – either monthly, quarterly, or every six months. Reinvesting your dividends in the same ETF might be an option.
ETFs, come with risks that are similar to those of mutual funds and stocks. ETFs, like most other investment instruments, can be low-, moderate or high-risk. As a result, you may even end up losing money through your ETF if you don’t play your cards right. While bonds offer reasonably predictable returns, investing in individual bonds is not easy for regular investors.
ETFs can make for fitting investments, provided one is selective about the process. This requires that you understand the underlying index, look at the volatility involved, and compare it with other indices. Aspects that need your attention when selecting suitable ETFs include:
Beginners may benefit by investing in ETFs owing to factors such as a range of alternatives, easy liquidity, low expense ratios, low investment thresholds, and the ability to diversify.
ETFs come with no minimum investment requirements. However, just how much you should invest depends on your income, wealth, and portfolio’s existing asset allocation.
The main benefits of investing in ETFs include:
The drawbacks linked to ETFs include:
 I start the financial planning and investment process by understanding your goals and objectives while also considering your risk tolerance.
I start the financial planning and investment process by understanding your goals and objectives while also considering your risk tolerance.
I can help you construct a robust portfolio and measure its progress while reviewing and rebalancing it regularly.
Get on the path to wealth creation by seeking your first free consultation now.
Author, Blogger & Independent Financial Advisor. My goal is to give you actionable tools for creating passive income and building wealth. More than 10,000 expats have already used my ideas to jumpstart their journey towards financial independence. Connect with me to start yours...

"Mutual funds were created to make investing easy, so consumers wouldn't have to be burdened with...

"Do not put all your eggs in one basket."
We have heard this before,...

Zurich Simple Wealth, as the name suggests is a simple & straightforward lump-sum investment plan...